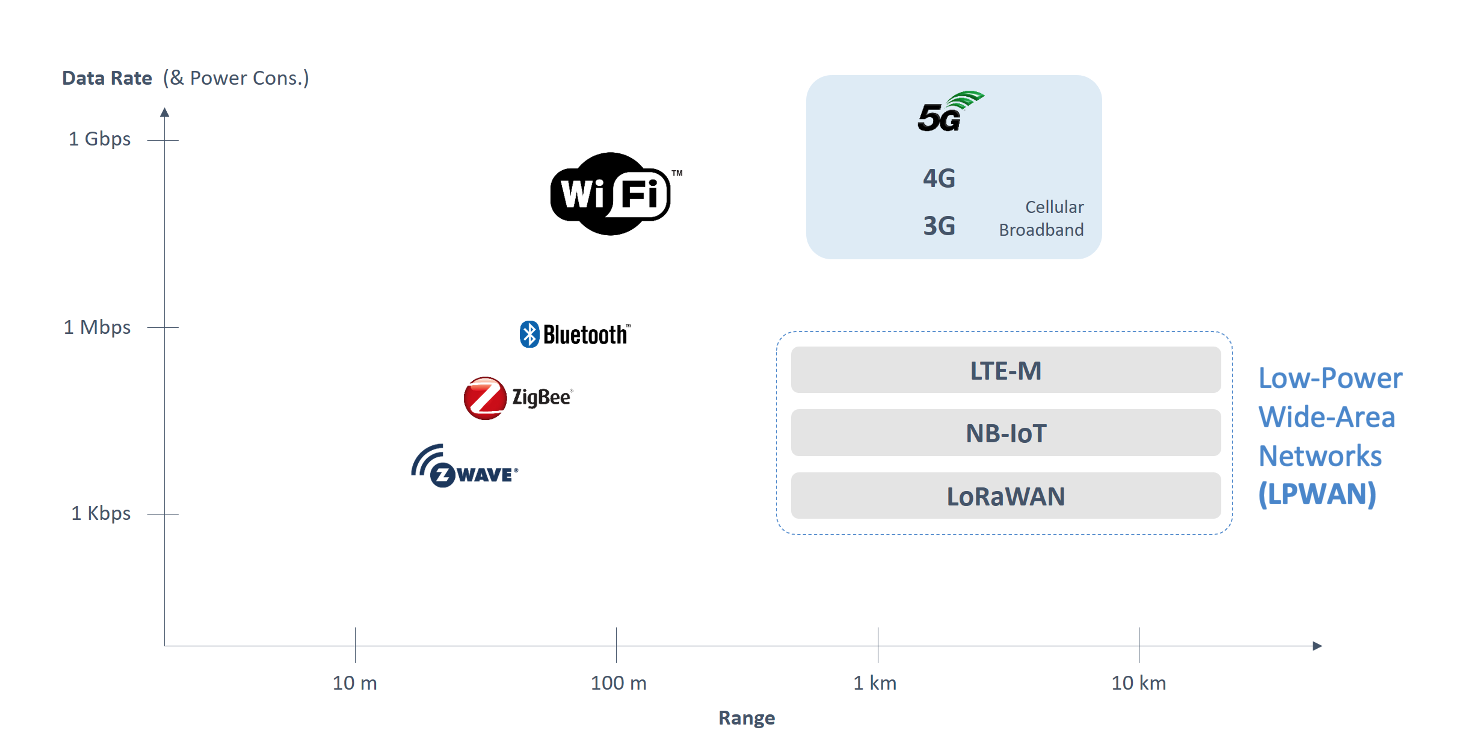
There is a plethora of options when we consider the whole spectrum of communication technologies. Figure 2.1 depicts a transmission-range versus data-rate plot, where higher data rate also typically translates to higher power consumption. On the top, we see the well-known broadband connection technologies, wireless local area network (WiFi) to the left and the wide area cellular network technologies (3G, 4G, 5G) to the right. On the bottom left, we have the so-called personal area network technologies, such as Bluetooth and Zigbee.
At the bottom right of the figure, we have the so-called Low Power Wide Area Networks, most suitable for Massive IoT, since they provide large coverage/range with much lower power consumption. Aligned with our focus on massive IoT applications in this module, the rest of the lecture focuses on “Low-Power Wide-Area Network” (LPWAN) technologies.
In Figure 2.2, we see another visualization, in the form of a spider web, which illustrates how LPWAN technologies address the target characteristics of Massive IoT applications, in comparison with ZigBee and cellular network technologies.
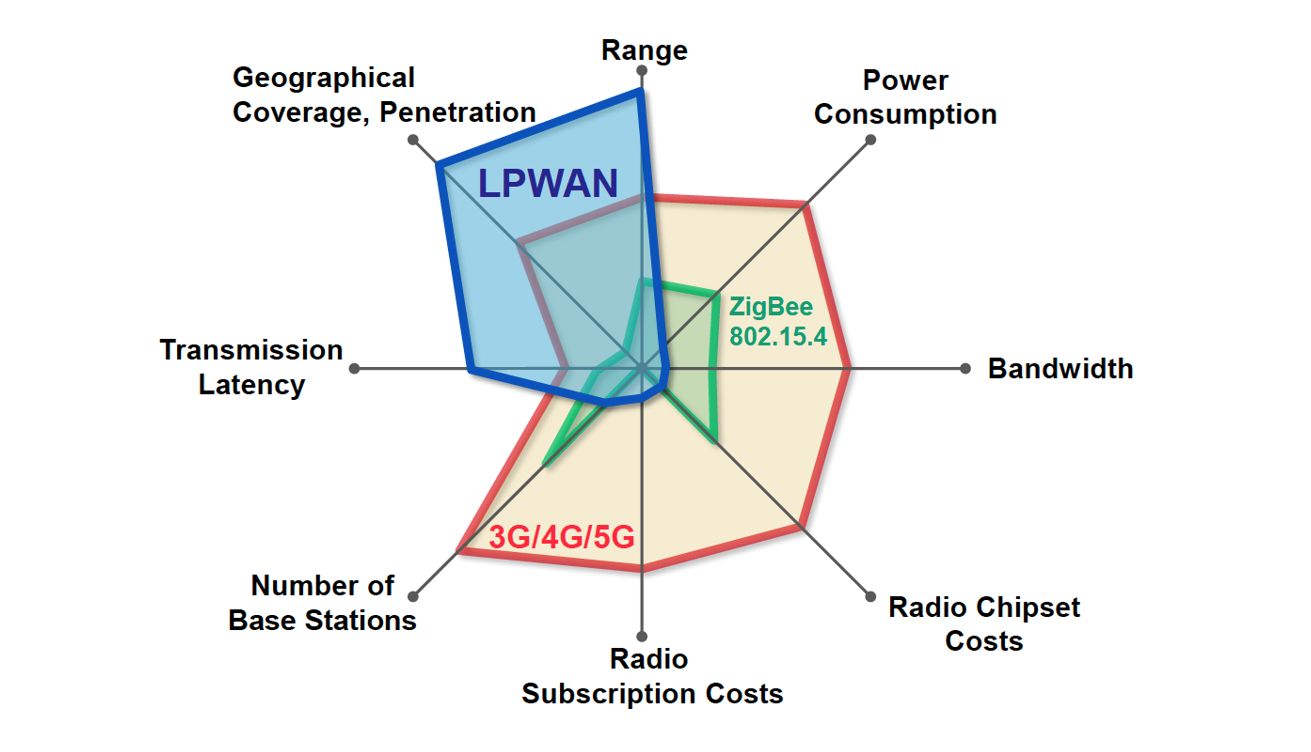
We observe from the figure that LPWAN technologies have
- (longer) range and coverage,
- (lower) power consumption,
- (smaller) number of base stations required, and
- (lower) radio costs,
at the expense of (higher) latency and (lower) data rates.
¶ 2.1 Diverse Set of LPWAN Technologies
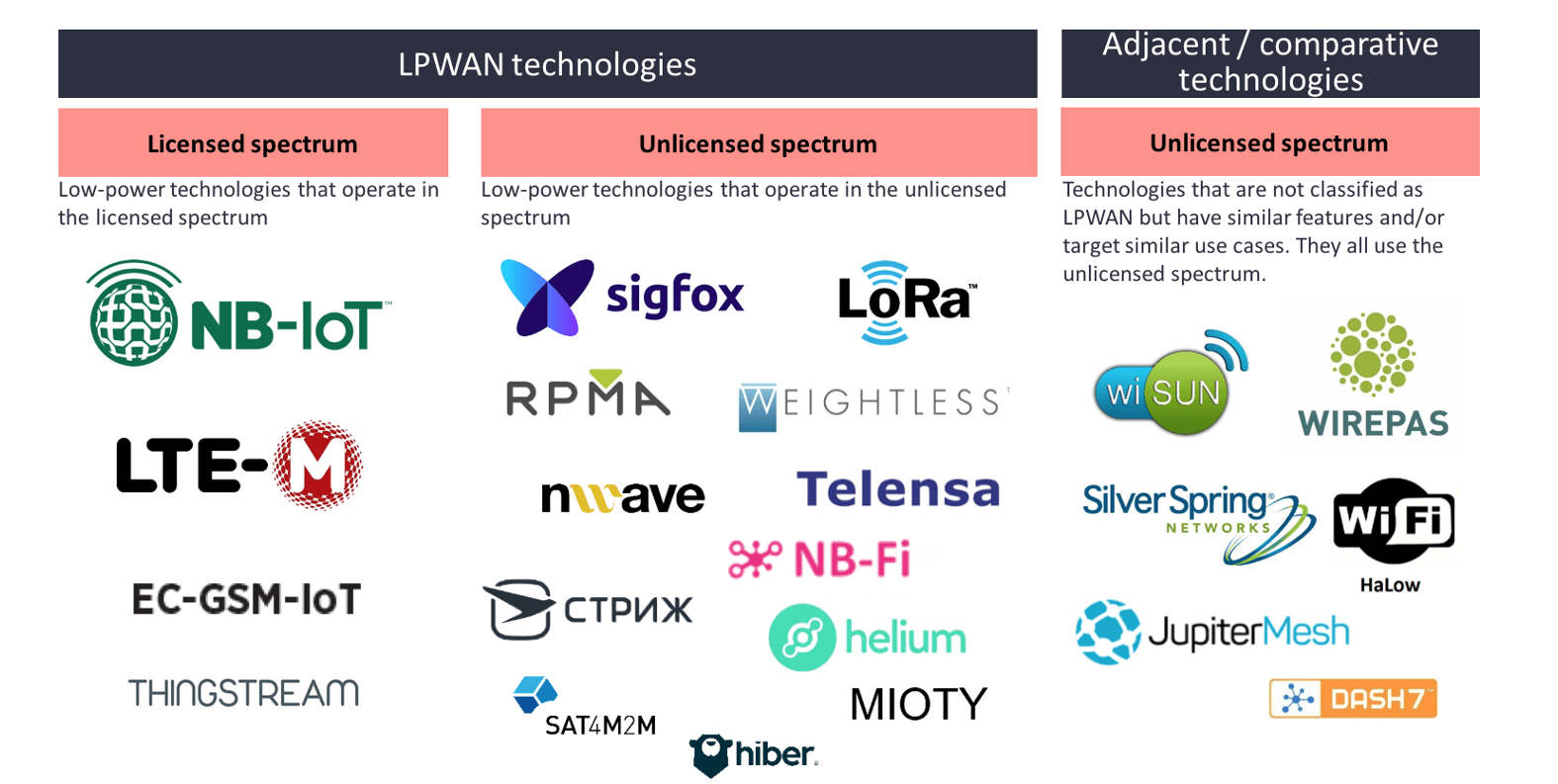
There are many different LPWAN technologies, some of which are shown in Figure 2.3. This includes some other technologies that may also be used for IoT with similar features to LPWAN specifications.
Here it is important to note the distinction between technologies operating in the licensed vs. unlicensed spectrum:
- Licensed spectrum case means only the network operators who own the licenses for certain wireless frequency bands can deploy and operate those technologies.
- In the unlicensed spectrum case on the other hand, anyone can deploy and operate networks in designated frequency bands, as long as they respect certain regulations about the transmission power and duty cycles.
It is also worth noting that Satellite IoT is expected to be an emerging alternative or complementary to terrestrial systems.
Although there are numerous connectivity technologies, especially under the unlicensed spectrum, only four of these technologies (namely, NB-IoT, LTE-M, Sigfox and LoRa) account for over 90% of all LPWAN connections worldwide (IoT Analytics, 2019). When we have a closer look at the market adoption of those LPWAN technologies, as depicted in Figure 2.4, we see that the two technologies, LoRa and NB-IoT, have a clearly larger market share. Therefore, we will cover these two technologies in the rest of the lecture.
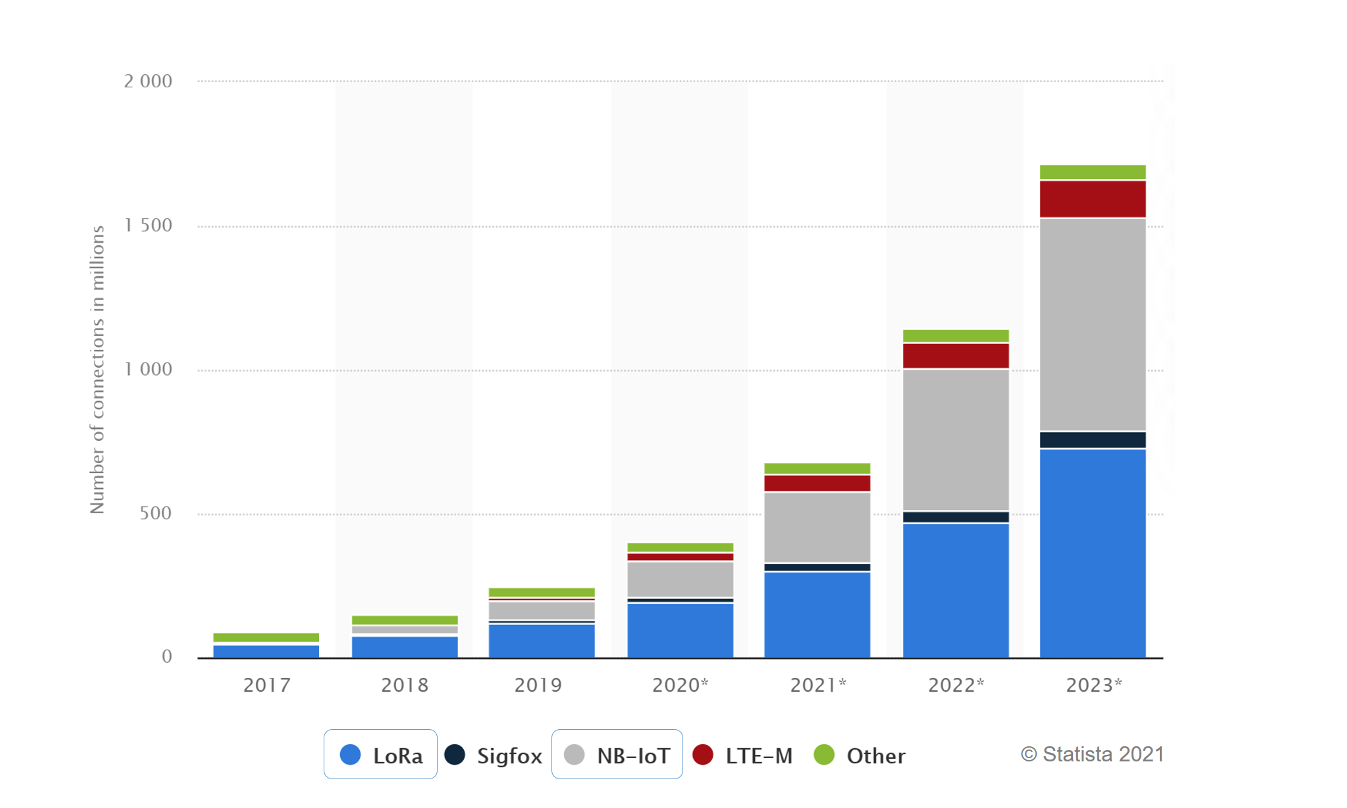
Figure 2.4: Adoption rates of popular LPWAN technologies; LoRa and NB-IoT up front with a clear margin